If you need any help, please feel free to contact us
- Silver Alloy Electrical Contact Materials
- Copper Alloy Electrical Contact Materials
- Multi-layer Composite Materials
- Special Type Of Wire
- Thermal Bimetal Material
- Copper Steel Composite Material
- Copper Aluminum Composite Material
- Silver Copper Composite Material
- Copper Nickel Composite Material
- Aluminum Nickel Composite Material
- Aluminum Steel Composite Material
- Noble Metal Complex
Effective Techniques for Cutting Tungsten Carbide Rods/Bars
Introduction
Tungsten carbide bars and rods are widely used in industries requiring extreme hardness, wear resistance, and thermal stability — such as tooling, machining, mining, and electronics. These materials are prized for their durability but are notoriously difficult to cut and machine due to their exceptional hardness. Understanding the appropriate methods for cutting tungsten carbide bars is crucial for maintaining tool integrity, minimizing waste, and ensuring precision in final applications.
This article delves deep into the practical methods, tools, and best practices for cutting tungsten carbide rods and bars efficiently and safely.
Understanding Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide is a composite material composed mainly of tungsten and carbon atoms. Its hardness approaches that of diamonds, with a Mohs hardness of about 8.5-9. It boasts superior resistance to wear, corrosion, and high temperatures. However, these properties make tungsten carbide incredibly challenging to cut using conventional methods. Attempting to cut it with standard metalworking tools often results in tool damage, poor finishes, and material wastage.
Why Cutting Tungsten Carbide is Challenging
Extreme hardness: Standard steel or carbide tools wear out quickly.
Brittleness: Though hard, tungsten carbide is brittle and prone to cracking or chipping if stressed improperly.
Heat sensitivity: Excessive heat generated during cutting can cause microfractures or thermal damage.
These challenges require specialized cutting methods designed to minimize mechanical stress and dissipate heat effectively.
Popular Methods for Cutting Tungsten Carbide Bars and Rods
1. Diamond Saw Cutting
Diamond saw blades are the industry standard for cutting tungsten carbide bars and rods.
How it works: Diamond particles are bonded to the saw blade's edge, allowing them to grind through the carbide material.
Benefits: High precision, clean cuts with minimal chipping, and efficient material removal.
Best practices:
Use continuous water cooling to dissipate heat and reduce blade wear.
Maintain a slow feed rate to avoid cracks.
Choose a blade size appropriate for the diameter of the tungsten carbide rod or bar.
Applications: Cutting tungsten carbide rods into smaller lengths, trimming bars for tooling applications.
2. Wire EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining)
Wire EDM is a non-contact cutting method using electrical discharges (sparks) to erode material.
How it works: A thin wire acts as an electrode, moving precisely while electrical sparks melt the tungsten carbide.
Benefits: Exceptional precision, smooth surface finish, no mechanical stress, suitable for complex shapes.
Limitations: Slow process, higher cost, limited to conductive materials (tungsten carbide is conductive).
Best practices: Ensure the carbide bar is properly secured; use optimal dielectric fluid and machine parameters for best results.
3. Grinding
Grinding using diamond-coated wheels or belt grinders is another way to shape or cut tungsten carbide bars.
How it works: Abrasive grains cut the surface by mechanical abrasion.
Benefits: Good surface finish, can produce complex shapes, precise dimensional control.
Limitations: Slower material removal rates, requires skilled operators.
Best practices: Use diamond abrasives, apply coolant consistently, and avoid excessive pressure to prevent cracks.
4. Laser Cutting (Limited Use)
Laser cutting tungsten carbide is possible but uncommon.
How it works: High-powered lasers vaporize or melt the material.
Limitations: Tungsten carbide’s thermal conductivity can cause uneven heating and cracking. Also, expensive and less precise for thick bars.
Best practices: Use in conjunction with other methods or for thinner sections only.
Equipment Recommendations for Cutting Tungsten Carbide Bars
Diamond-tipped circular saws with water cooling systems.
Precision Wire EDM machines for detailed cuts.
Diamond grinding wheels and belt grinders for finishing.
Proper workholding devices to secure rods and bars firmly.
Safety Considerations
Always wear eye protection to guard against flying debris.
Use water or coolant to minimize dust and heat.
Handle tungsten carbide dust carefully, as it can be hazardous if inhaled.
Ensure machines have proper ventilation and dust extraction.
Summary and Best Practices
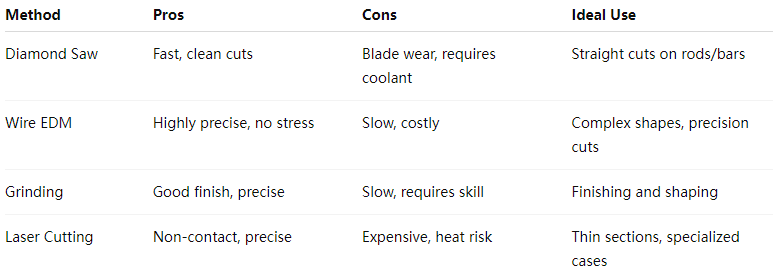
For most applications, diamond saw cutting combined with water cooling is the most practical and cost-effective way to cut tungsten carbide rods and bars.
Final Thoughts
Cutting tungsten carbide bars and rods requires careful selection of methods and tools to overcome the material's hardness and brittleness. Diamond cutting techniques, such as saw blades and grinding wheels, dominate the industry for their balance of efficiency and precision. For highly intricate work, Wire EDM provides unmatched accuracy, albeit at higher cost and slower speeds.
By following the recommended practices and safety measures, machinists and engineers can successfully cut tungsten carbide bars and rods while preserving material integrity and tool longevity.
- Tel:
+86-18857735580 - E-mail:
[email protected]
- Add:
No. 5600, Oujin Avenue, Wenzhou Marine Economic Development Demonstration Zone, Zhejiang Province, China
Copyright © Wenzhou Hongfeng Electrical Alloy Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Metal Composite Materials Manufacturers

 en
en English
English Deutsch
Deutsch