If you need any help, please feel free to contact us
- Silver Alloy Electrical Contact Materials
- Copper Alloy Electrical Contact Materials
- Multi-layer Composite Materials
- Special Type Of Wire
- Thermal Bimetal Material
- Copper Steel Composite Material
- Copper Aluminum Composite Material
- Silver Copper Composite Material
- Copper Nickel Composite Material
- Aluminum Nickel Composite Material
- Aluminum Steel Composite Material
- Noble Metal Complex
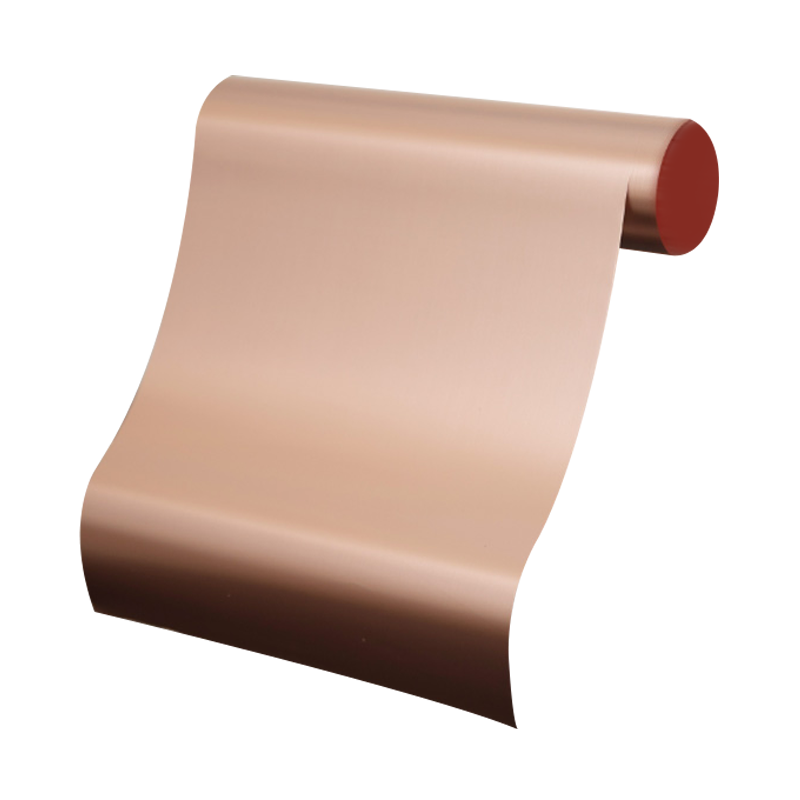
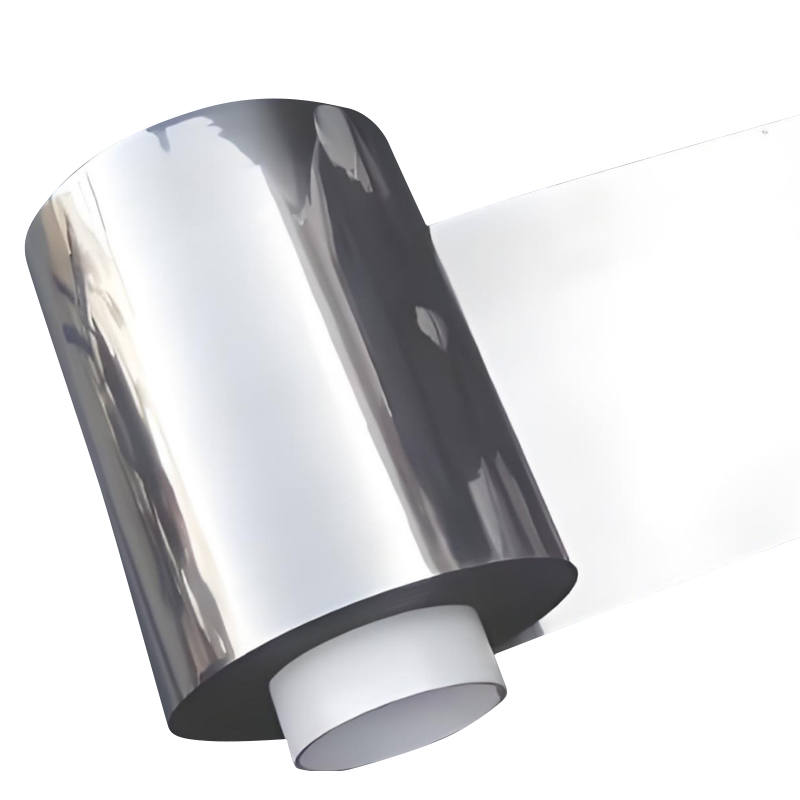
Understanding the Key Differences Between Rolled Copper Foil and ED Copper Foil in PCB Manufacturing
Rolled copper foil and electrodeposited (ED) copper foil are two primary forms used in printed circuit board (PCB) manufacturing, each with distinct characteristics that influence performance and application suitability. Rolled copper foil is produced through a mechanical rolling process that compresses copper ingots into thin, uniform sheets. This method results in a dense microstructure with excellent mechanical strength and consistent thickness, making it ideal for applications where durability and precision are critical. In contrast, ED copper foil is created through an electroplating process, which deposits copper ions onto a rotating drum, forming a foil with a more columnar grain structure.
The structural differences between rolled copper foil and ED copper foil directly affect their electrical and thermal conductivity. Rolled copper foil generally exhibits slightly lower conductivity than ED foil due to its work-hardened state from the rolling process. However, this same hardening gives rolled copper foil superior tensile strength and resistance to deformation under stress—advantages that come into play in high-reliability sectors such as aerospace and automotive electronics. ED foil, while softer and more ductile, may be more prone to tearing or stretching during PCB lamination processes.
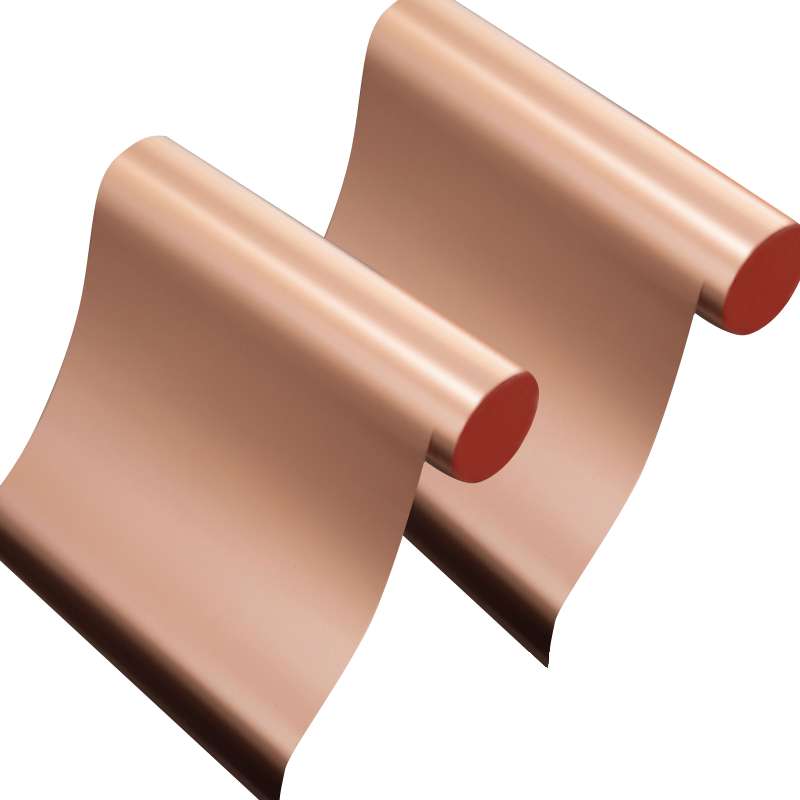
Surface morphology is another crucial factor when choosing between these materials. Rolled copper foil typically has a smoother, flatter surface finish, which contributes to better signal integrity in high-frequency circuits. This smoothness reduces skin effect losses and minimizes impedance variations, especially in RF and microwave applications. ED copper foil, on the other hand, tends to have a rougher surface texture due to its crystalline growth pattern, which can enhance adhesion to dielectric layers but may also introduce signal scattering issues at higher frequencies.
From a manufacturing perspective, rolled copper foil offers greater dimensional stability. Its predictable behavior during etching and plating makes it a preferred choice for fine-line circuitry and controlled-impedance designs. The material's low coefficient of thermal expansion helps maintain trace alignment over temperature fluctuations, reducing the risk of delamination or circuit failure. These properties make rolled copper foil particularly well-suited for rigid PCBs and high-speed digital circuits where signal fidelity is paramount.
Despite its advantages, rolled copper foil is often more expensive than ED foil due to the energy-intensive rolling process and tighter quality control required. For cost-sensitive applications or where extreme flexibility isn’t necessary, ED copper foil remains a popular option. That said, manufacturers who prioritize long-term reliability and performance in demanding environments increasingly opt for rolled copper foil to ensure product longevity and compliance with industry standards like IPC-4562.
As global demand for high-performance electronics continues to rise, the choice between rolled copper foil and ED copper foil becomes more strategic. Whether you're developing advanced communication devices, industrial control systems, or next-gen consumer electronics, understanding these material differences allows for smarter design decisions and optimized production outcomes. At our facility, we specialize in delivering high-quality rolled copper foil tailored to meet the evolving needs of modern PCB fabrication.
Choosing the right rolled copper foil isn't just about meeting specifications—it's about ensuring your end products perform reliably in real-world conditions. With years of experience in producing precision rolled copper foil, we provide technical support and customized solutions to help you select the best material for your unique application. Trust in proven performance and partner with a manufacturer committed to excellence in every roll.
- Tel:
+86-18857735580 - E-mail:
[email protected]
- Add:
No. 5600, Oujin Avenue, Wenzhou Marine Economic Development Demonstration Zone, Zhejiang Province, China
Copyright © Wenzhou Hongfeng Electrical Alloy Co., Ltd. All Rights Reserved. Metal Composite Materials Manufacturers

 en
en English
English Deutsch
Deutsch